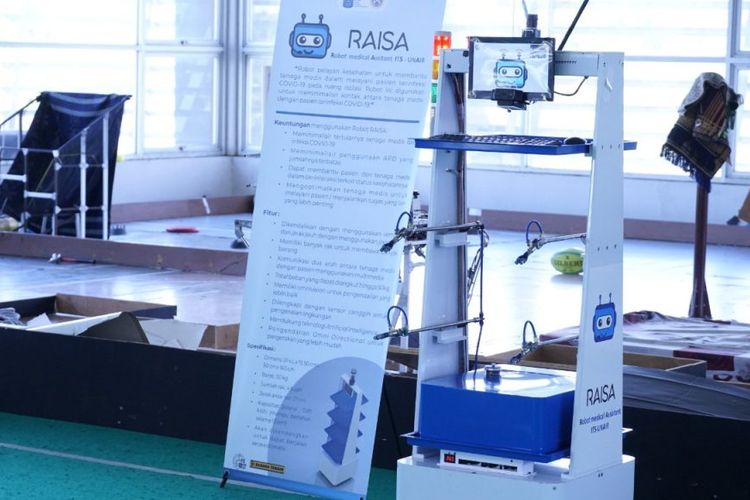

RAISA
Robot RAISA (Robot Medical Assistant ITS – Unair) is a robot made from collaboration effort from Institut Teknologi Sepuluh Nopember (ITS) and Universitas Airlangga. RAISA is a health service robot to help and minimize the contact of health workers with Corona patients, RAISA is designed to be able to send various patient needs, ranging from medicine, personal protective equipment in the form of face shields, food, and so on. RAISA has a height of 1.5 meters, with battery specification of 0.85 kWh. This robot is equipped with four shelves that can carry a maximum of 50 kilograms of goods. In addition, there is a monitor that can be used for two-way communication between medical personnel and patients. Raisa's operation relies heavily on a WiFi connection. This robot is predicted to capable of lasting between 8-10 hours
Computer-aided Diagnosis System for Osteoporosis
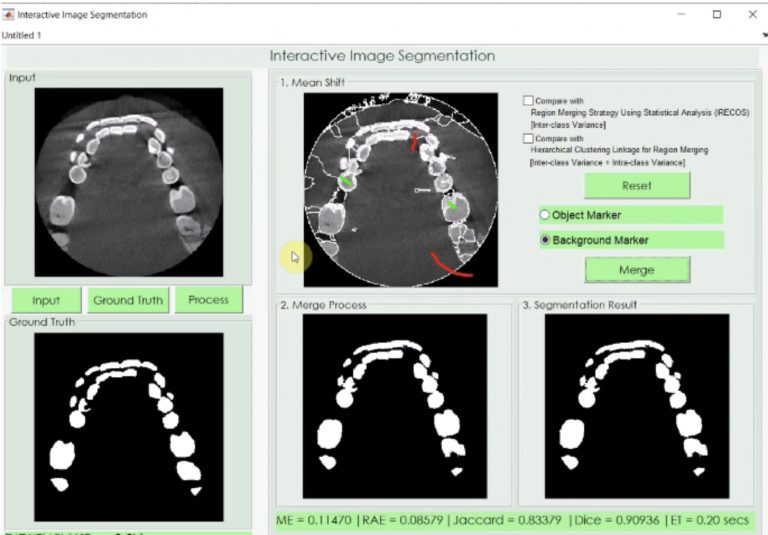
This product is based on a publication, but not limited to, "Computer-aided system for measuring the mandibular cortical width on panoramic radiographs in osteoporosis diagnosis". Automatic measurement of cortical width may enable us to identify a large number of asymptomatic women with low BMD. Initially, oral radiologists determined the region of interest based on the position of mental foramen. Some enhancing image techniques were applied so as to measure the cortical width at the best point. Panoramic radiographs of 100 women who had BMD assessments of the lumbar spine and femoral neck were used to confirm the efficacy of our new system. Cortical width measured with our system was compared with skeletal BMD. There were significant correlation between cortical width measured with our system and skeletal BMD. These correlations were similar with those between cortical width manually measured by the dentist and skeletal BMD. Our new system may be useful for mass screening of osteoporosis.

Computer-aided Diagnosis System for Leukemia Types
A fuzzy feature representation for white blood cell differential counting is proposed to diagnose types of acute leukemia. The accuracy of diagnosis is higher than that by numerical features by dealing with uncertainty of white blood cell features and inflexibility of diagnosing. Experiments on acute leukemia diagnosis use 120 acute leukemia images and fuzzy decision tree method with the accuracy rate of diagnosis is 84% using fuzzy features and 76.6% using numerical features. Given the importance of accurate diagnosis of acute leukemia in patients, this proposal is essential and planned to be introduced in an Indonesian hospital.
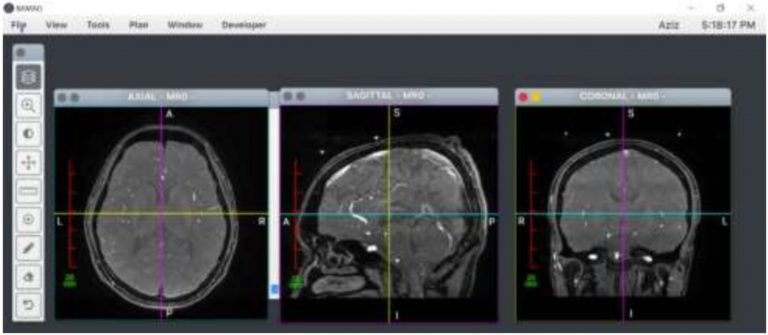
Developing Accurate 3D Additive Manufacturing Generator based on Medical Images for Planning Cranioplasty Surgery and Craniofacial Reconstruction Surgery
This product is based on a publication, but not limited to, "Corpus Callosum Segmentation from Brain MRI Images Based on Levet Set Method", "Multilevel thresholding and Morphological Relationship Approach for Automatic Detection of Anterior and Posterior Commissure in Mid-sagittal Brain MRI" and Brain Segmentation using Adaptive Thresholding, K-Means Clustering and Mathematical Morphology in MRI Data".

S – Analyzer Smart System to Determine Motility and Morphology Abnormalies of Spermatozoa
This product is based on a publication, but not limited to, "Modified Background Subtraction Statistic Models for Improvement Detection and Counting of Active Spermatozoa Motility". An important early stage in the research of sperm analysis is the phase of sperm detection or separating sperm objects from images/video obtained from observations on semen. The success rate in separating sperm objects from semenfluids has an important role for further analysis of sperm objects. Algorithm or Background subtraction method is a process that can be used to separate moving objects (foreground) and background on sperm video data that tend to uni-modal. In this research, some of the subproject model statistics of substrata model are Gaussian single, Gaussian Mixture Model (GMM), Kernel Density Estimation and compared with some basic subtraction model background algorithm in detecting and counting the number of active spermatozoa. From the results of the tests, the Grimson GMM method has anf-measure value of 0.8265and succeeded in extracting the sperm form near its original form compared to other methods.

InViSiMoS Integrated Vital Sign Monitoring System
Invisimos, or the Integrated Vital Sign Monitoring System, allows medical personnel to monitor all inpatients throughout the ward at once because Invisimos has an external port that can transmit the patient's vital conditions in real time using the hospital's local ethernet / LAN network. If there is an emergency, medical personnel can also immediately know and act immediately without being called. This system is very much needed to support health services, especially in hospitals with shortages of labor. With fast and accurate monitoring of the patient's condition, patient care can be improved.

TB- Analyzer Smart Device to Count TB Bacteria
This product is based on a publication, but not limited to, "Comparison of Tuberculosis Bacteria Classification from Digital Image of Sputum Smears". Positive and negative tuberculosis was determined by the amount of bacteria found in sputum. Microscopic analysis is known to have weaknesses in distinguishing between tuberculosis bacterias. Also in counting the number of bacteria seen in the microscope because the tendency of it to accumulate together. In addition, manual counting of tuberculosis bacteria takes a lot of time, require high concentration and labor-intensive. We provide automated systems to distinguish between single and multiple tuberculosis bacteria and non-bacterial ones. The compared methods are backpropagation and K-nearest neighbor (KNN). Sputum sample digital images are converted to HSV color channels. The bacterial length and bacterial endpoint is a feature that is extracted from tuberculosis bacteria. This unique feature is used to classify which one is belong to single bacteria and which one is included as double bacteria. Based on the experimental results, both methods can be used to classify single bacteria and double bacteria with 93.22% accuracy for backpropagation and 94.92% for KNN. So K- NN method better than backpropagation method for classifying tuberculosis bacteria.
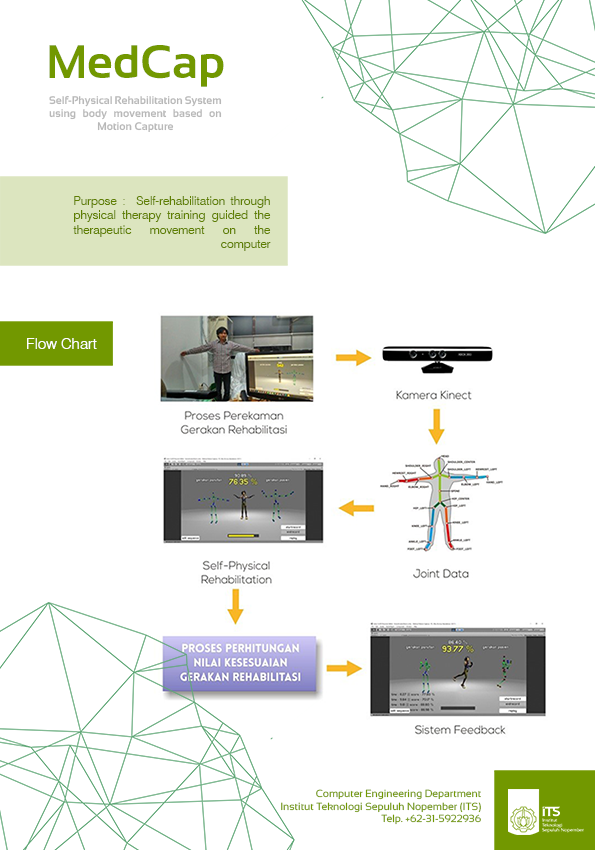
MedCap Motion Capture for Medical Rehabilitation
With a computer and a kinect (stereovision) camera, the research team designed a 3D physiotherapist application that works by capturing images using two different viewing angles. Kinect has two main cameras, namely a depth camera and an RGB camera, and an infrared transmitter. The depth camera is used to determine the depth distance of the object from the camera, while the RGB camera is used to determine the shape of the object's texture or surface. The way MedCap works is to record the movements of a physiotherapist, then these movements are stored in memory and manipulated by a 3D avatar. The patient will mimic the movement of the avatar that appears on the monitor by emphasizing the position of the movement in three coordinate axes, namely the x, y, and z axes. The patient's movements will be assessed automatically based on the degree of similarity, agility and flexibility. So far, the Kinect camera is only able to capture the movements of a person who has a posture height of between 1.5 - 2 meters and an optimal distance of 2 meters from the camera, so it still needs more development.